Bluetooth barrages
Hacking Bluetooth, a wireless voice and data transmission technology, which can be found in mobile phones, PDAs, USB sticks, keyboards, mices, headsets, printers, telephone facilities in cars, navigation systems, new modern advertisement posters, umbrellas, basket, socker and golfballs, and fridge magnets.
The design of Bluetooth pays a lot of attention to security. The connection can be encrypted and authenticated. The address is set by the device firmware and not by the OS kernel, which makes address spoofing harder but not impossible.
A device can be set into non-discoverable mode for it to not show up in a scan result.
The protocol stack is so complex that various vulnerabilities have come up in all common Bluetooth implementations like Android, iOS, Windows and Linux.
It is now common for radioing devices to appear in the craziest places.
Protocol stacks
Bluetooth is a wireless voice and data transmission technology, which can be found in mobile phones, PDAs, USB sticks, keyboards, mices, headsets, printers, telephone facilities in cars, navigation systems, new modern advertisement posters, umbrellas, washing machines, cat litter trays, fragrance dispensers, deodorant sticks, toilets, salt shakers, you name it.
Classic Bluetooth protocol stack
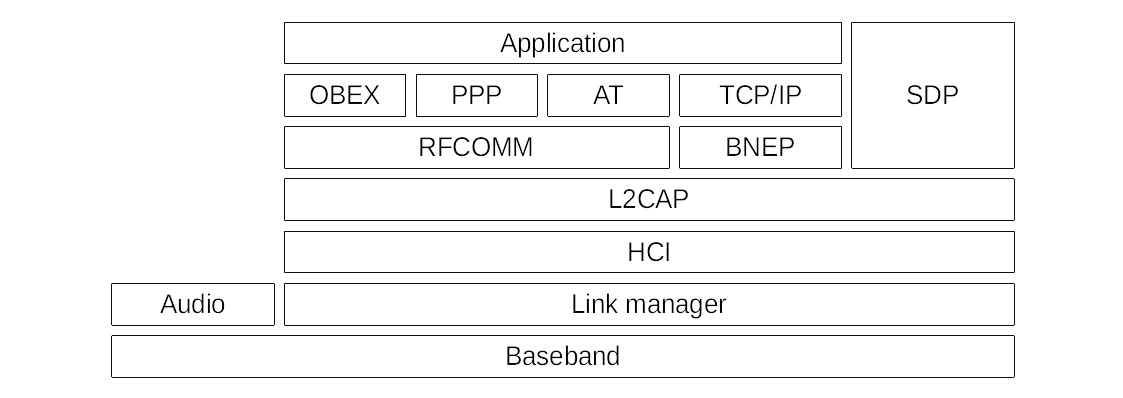
The baseband is built by the radio interface. It operates on the 2.4 GHz ISM band (2400–2483.5 MHz) with a signal strength of 1 mW–100 mW and a range of 1–100 m. With the right antenna you can extend the range up to a mile. The baseband is divided into 79 channels and switches frequency 1600 times per second. This is called Frequency-Hopping; it increases the robustness against interferences and makes sniffing more difficult.
The Link Manager Protocol (LMP), can be compared with Ethernet and implements a 48-bit long Bluetooth source and destination address that consists of three parts NAP, UAP and LAP. As with MAC addresses the first three byte are vendor specific. LMP is also responsible for the link setup, authentication and encryption and the pairing process (negotiate a long term key used to derive session keys). It is implemented in the firmware of the Bluetooth hardware and knows 4 different security modes:
No encryption, no authentication
Individual traffic is verschlüsselt, Broadcast traffic is not, no authentication
All traffic is encrypted and authenticated
All traffic is encrypted and authenticated and uses Secure Simple Pairing (SSP, introduced in Bluetooth 2.1)
The Host Control Interface (HCI) implements an interface to the Bluetooth firmware. It is used to send L2CAP packets to the Link Manager in the firmware, to read features of the hardware and to change its configuration. It is the lowest layer that is implemented in the OS. The communication is packet- and connection-oriented.
The Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) is comparable to IP, and responsible for the fragmentation of data, group management and to implement higher layered protocols like RFCOMM, SDP or BNEP.
RFCOMM simulates a serial line and is not only useful to access serial devices such as modems in mobile phones. Higher layer protocols like OBEX depend on it. It is similar to TCP, as it implements channels for different applications. Via channels, programs (in Bluetooth called profiles)can be accessed. In total there are 30 channels.
The Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol (BNEP) encapsulates IPv4-, IPv6- or IPX- packets and tunnels it over TCP/IP. On Linux this is realized with pand. BNEP builds on L2CAP.
The Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) can be used to query the services of a remote device. Services must be registered to be listed. SDP builds on L2CAP.
OBject EXchange (OBEX) was invented to transfer objects. Differentiate between the OBEX-Push- and OBEX-Ftp-profile. OBEX-Push is commonly used for instant ad-hoc data transfer like sending vcards. OBEX-Ftp is more like FTP, to sync whole directory structures. There are other OBEX based profiles. OBEX builds on top of RFCOMM.
BLE – Bluetooth Low Energy
Since Version 4.0 there is another protocol stack called Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) historically also named Bluetooth Smart. Originally it was invented for IoT devices, which have small battery capacity and only want to exchange data from time to time over a low distance like fitness trackers, medical devices, sensors and so on. Every smartphone and Bluetooth chip in laptops have BLE included.
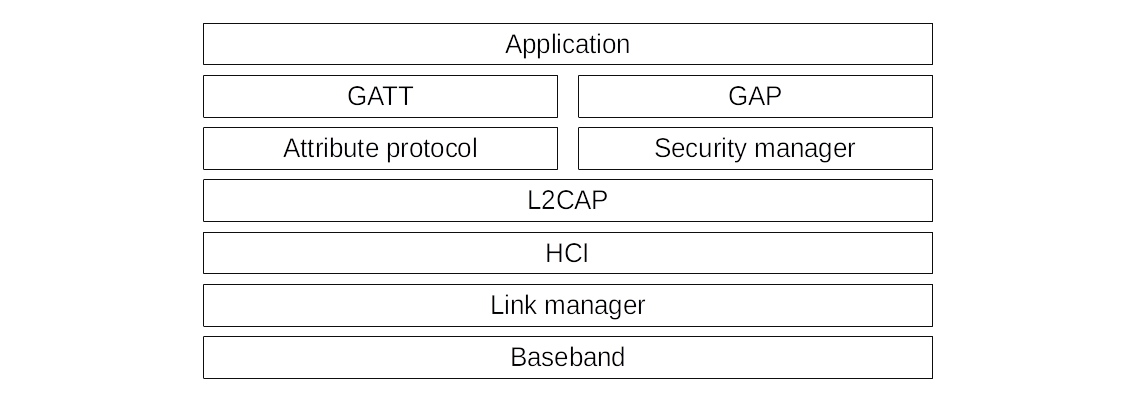
The Generic Access Profile (GAP), defines new roles for communication: Peripheral (sends advertisements and is connectable), Central (scans for advertisements and connects to a peripheral), Broadcaster (also sends out advertisements, but is not connectable), and last but not least, Observer (receives advertisements, but cannot initiate a connection). Peripherals and Broadcaster are sometimes also called Beacons. Peripherals can implement a whitelist of addresses of Bluetooth devices allowed to find them in a discovery scan and to connect to them. This can be circumvented by a hardware Bluetooth sniffer like Ubertooth and Address-Spoofing.
the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT), builds on the ATT protocol and is used to read and write values. It implements them in a hierarchy of different services with a number of characteristics. Beside reading and writing data GATT can also be used to send commands as well as notifications and indications of data it manages. Indication and notification packets are used to inform about new or updated data. Indication packets must be acknowledged by the client.
BLE devices typically do not have enough computing power to do encryption. If encryption is in use often a hard coded pin such as 0000 or 1234 is used due to the lack of a keyboard. The spec also defines the possibility to generate a random pin during the pairing process. Another option of many BLE devices is using bonding. It means paired devices store the key and use them for later communication.
Device discovery
Check bluetooth device is up
Scan
HCI
To verify you have a Bluetooth adapter:
hciconfig
If the Bluetooth adapter is not enabled, enable it (where hci0 is the interface ID):
hciconfig hci0 up
To scan for Bluetooth devices (close to you):
hcitool scan
Record the MAC address of a device in order to send commands to a device.
Simple python scanner script
The bt.discover_devices() function returns a list of tuples with the first item being
the hardware address and the second contains the device name if the parameter
lookup_names is set to True, otherwise the return value is just a list of addresses.
Bluetooth makes an extra connection just to resolve every name.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import bluetooth as bt
for (addr, name) in bt.discover_devices(lookup_names=True):
print("%s %s" % (addr, name))
Bluejacking
Bluejacking transmits data to a device without the knowledge of the user. This attack can be done by sending an electronic business card via Bluetooth to a target. Instead of putting a real name in the name field, insert a message.
Bluejacking is not inherently malicious, but takes a dark turn when used for sending phishing scams, or files that intend to hack or damage the device.
Enable the Bluetooth service
Enable the Bluetooth interface
Discover devices in the close environment
Impersonate Bluetooth information
Send message